Instruction-Tuned LLMs for Event Extraction
Research on enhancing event extraction using instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs), optimizing annotation guidelines, and improving fine-tuning techniques for NLP tasks.
---
Research conducted at George Mason University (GMU) - Natural Language Processing Lab
Research Advisor: Dr. Ziyu Yao
Authors: Saurabh Srivastava★, Sweta Pati★, Dr. Ziyu Yao [★ Equal contribution]
Conference Submission: ACL 2025
---
Research Paper & Resources:
- ACL 2025 (Findings): Instruction-Tuning LLMs for Event Extraction with Annotation Guidelines
- Research Institution: George Mason University (GMU), NLP Lab
- Research Advisor: Dr. Ziyu Yao
- Focus Area: Event Extraction, Instruction-Tuned LLMs, Annotation Guideline Generation, LLM FineTuning
- Code Repository: PyCode-TextEE
⚡ TL;DR: We instruction-tune LLMs for event extraction using Python code prompts and machine-generated annotation guidelines — achieving strong generalization across domains, schemas, and model sizes with minimal supervision.
Tech Stack & Tools:
- NLP and Machine Learning: LLaMA-3.1-8B, LLaMA-3.2-1B, and Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch, LoRA Fine-Tuning, Unsloth, Quantization
- Data Processing: JSON, Python (Pandas, Numpy)
- GPU Resources: HPC clusters, CUDA-enabled GPUs
- Evaluation Metrics: Precision, Recall, F1-score
Context & Motivation:
Event Extraction (EE) is a fundamental task in information extraction but remains challenging due to:
- Complex schemas
- Domain shifts
- Low-resource settings
Our work investigates how instruction-tuned LLMs can benefit from structured guidance in the form of event schemas and machine-generated annotation guidelines.
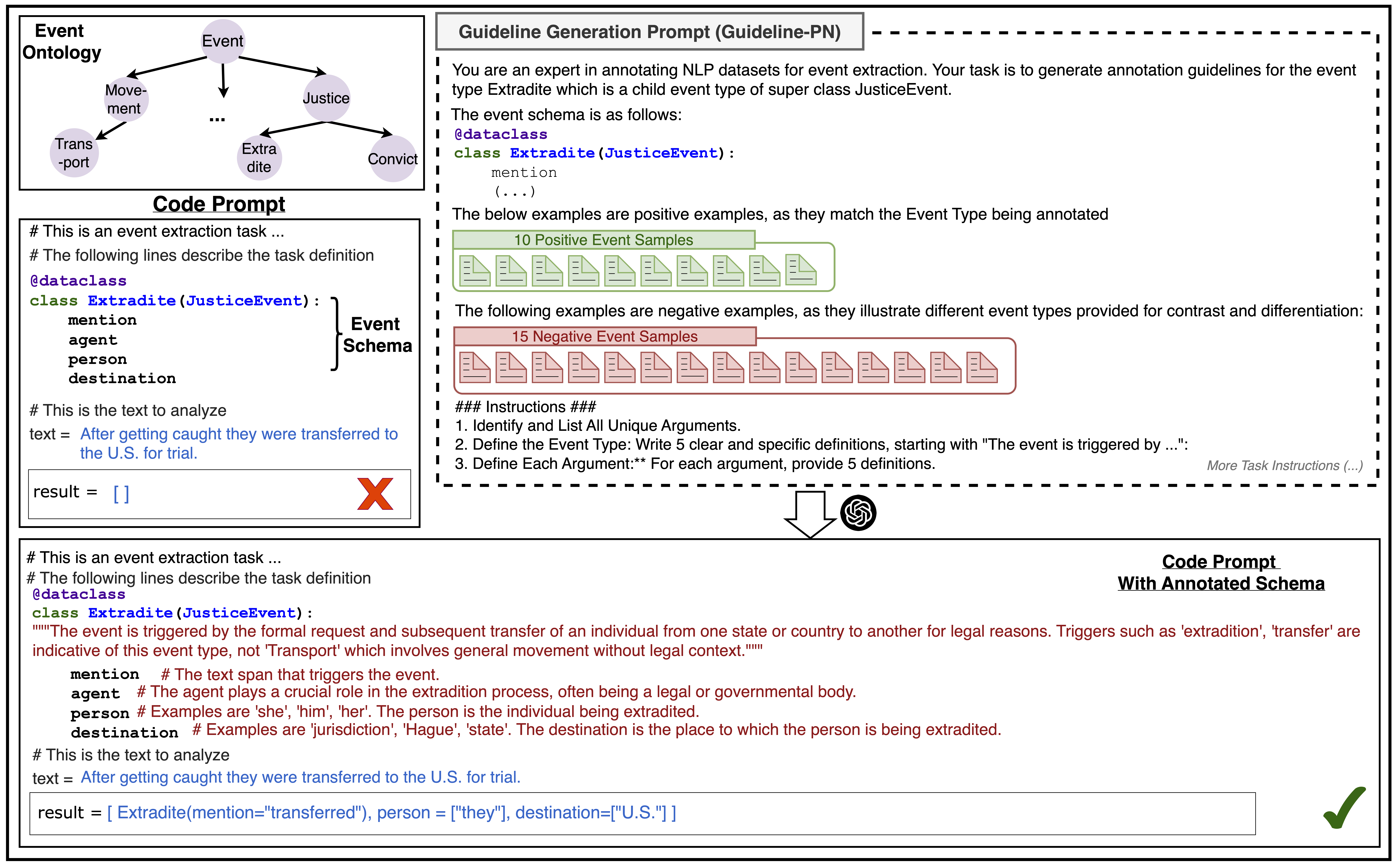
Approach:
This research explores the enhancement of event extraction (EE) tasks by leveraging instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs). Traditional event extraction models struggle with limited training data, ambiguous event definitions, and scalability. To address these challenges, our approach:
- Synthesized annotation guidelines using GPT-4o for:
- 500+ event types
- 4000+ argument structures
- Examples include positive, negative, and sibling event types
- Removes reliance on manually written guidelines

- Natural Language to Code-Based Prompt Conversion:
- We provide a modular conversion script that transforms natural language event extraction data (in TextEE format) into structured Python
@dataclassprompts with embedded annotation guidelines. - Instruction prompts use:
- We instruction-tune LLMs with structured prompts that represent events as Python
@dataclassdefinitions. - Annotation guidelines are integrated directly into prompt docstrings, defining triggers and arguments in natural language.
- We instruction-tune LLMs with structured prompts that represent events as Python
- We provide a modular conversion script that transforms natural language event extraction data (in TextEE format) into structured Python
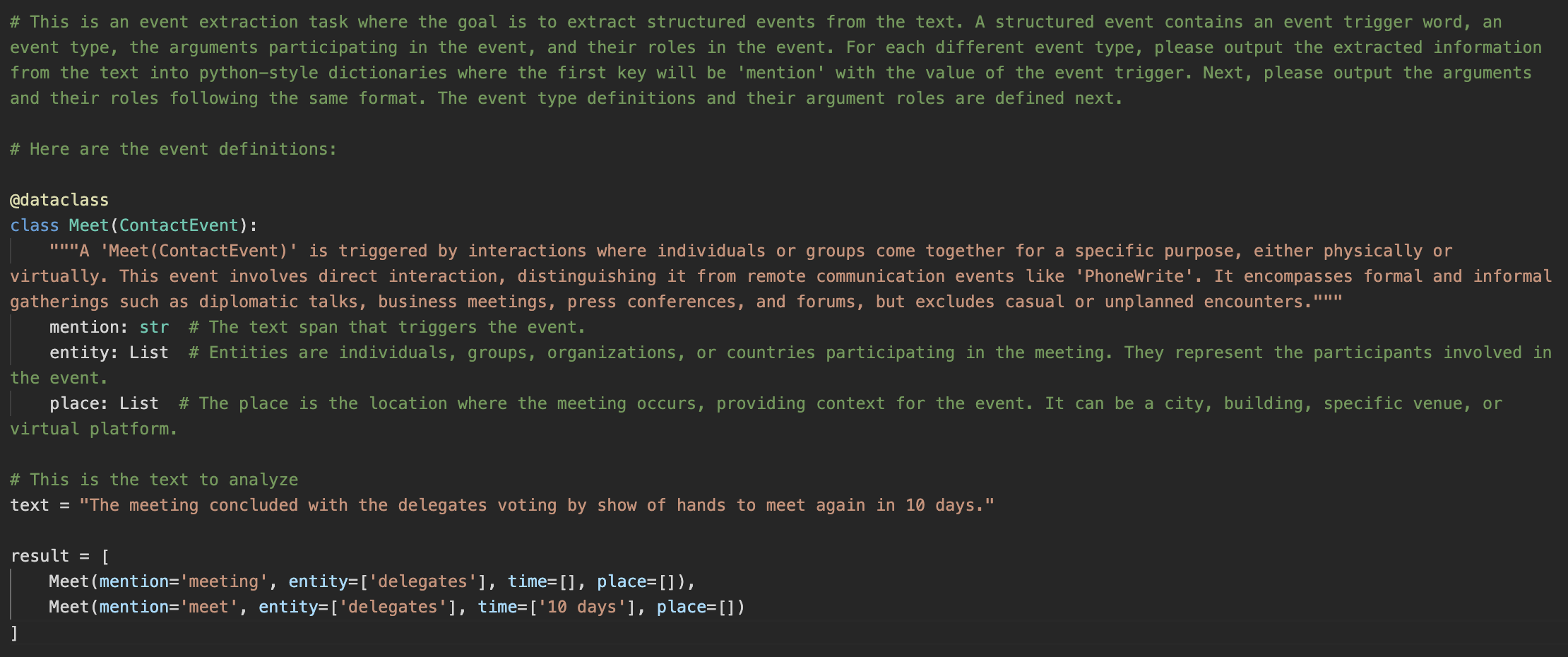
-
Fine-tuning models:
LLaMA-3.1 8B, LLaMA-3.2-1B, and Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B using LoRA and structured regularization -
Designed custom evaluation framework for EE tasks designed around structured code-like annotations
This work aims to improve F1-score performance on event extraction tasks and enhance the reliability of LLM-generated event predictions.
Experiments:
We conducted evaluations on:
- Datasets: ACE05 and RichERE
- Settings: Full-resource and low-resource (2k samples)
- Variants: With and without contrastive training (negative sampling)
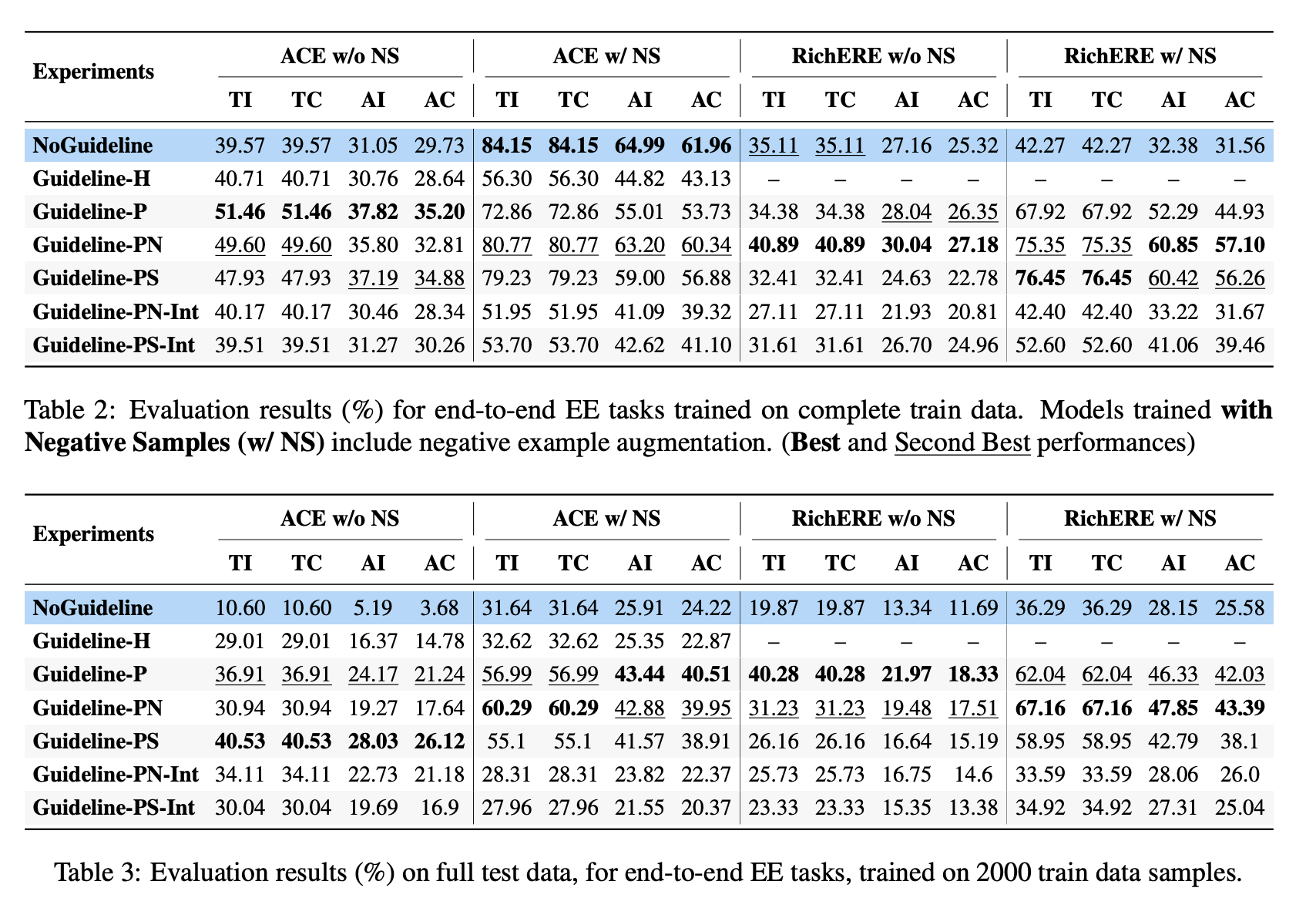
Key Results:
ACE05 (machine-generated guidelines, no negative sampling)
- Trigger Classification (TC): +10% improvement
- Argument Classification (AC): +5% improvement
RichERE (machine-generated guidelines, with negative sampling)
- Trigger Classification (TC): +30% improvement
- Argument Classification (AC): +25% improvement
Major Contributions
1. Annotation Guideline Optimization
- Developed a structured framework for creating high-quality event extraction annotation guidelines.
- Synthesized event schema covering 500+ event types and 4000+ argument structures using GPT-4o.
2. Natural Language to Code-Based Prompt Conversion:
- Developed a script that translates natural language event definitions into Python @dataclass-style code prompts
- These prompts include annotation guidelines as docstrings, making them executable and interpretable by LLMs
- Converts event triggers and arguments into Python-style classes
- Embeds natural language instructions as docstrings for each event type and role
- Supports automatic annotation guideline integration using synthesized or provided files
-
Generates LLM-compatible structured prompts for instruction tuning
- This script is a core part of the pipeline that bridges textual datasets and code-style prompt learning for LLMs like LLaMA-3 and Qwen.
3. LLM Fine-Tuning & Optimization
- Implemented Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for fine-tuning LLaMA-3.1 8B, LLaMA-3.2-1B, and Qwen2.5-Coder-1.5B on event extraction tasks using unsloth library.
- Improved model efficiency using structured regularization techniques.
4. Cost-Effective & Low-Latency Inference Pipelines
- Designed a scalable NLP pipeline using GPU-optimized environments.
- Designed a custom evaluation framework guided by annotations for each event type for event extraction tasks as code representations.
Performance Highlights:
- Machine-generated guidelines consistently outperformed human-written ones.
- The approach generalized well across domains, schema complexities, and model architectures.
- In low-data settings (2k), models with guidelines matched or exceeded full-data baselines.
- Frequent and moderately rare event types showed notable improvement, extremely rare types remain a challenge.
- While guidelines help, we found that machine-generated guidelines consistently outperform human-written ones, and their effectiveness may or may not complement negative sampling strategies.
Future Work & Applications
Expanding dataset coverage to include multi-domain event extraction tasks
Exploring multimodal event extraction by integrating text, images, and video content
For collaboration or inquiries, feel free to reach out via LinkedIn or Email.